This article explains the significance of resistor color codes and provides tips on how to identify them. The color bands on a resistor can convey important information such as resistance value, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. Knowing how to read these codes can help in selecting the right resistor for a circuit and troubleshooting potential issues.
How to identify
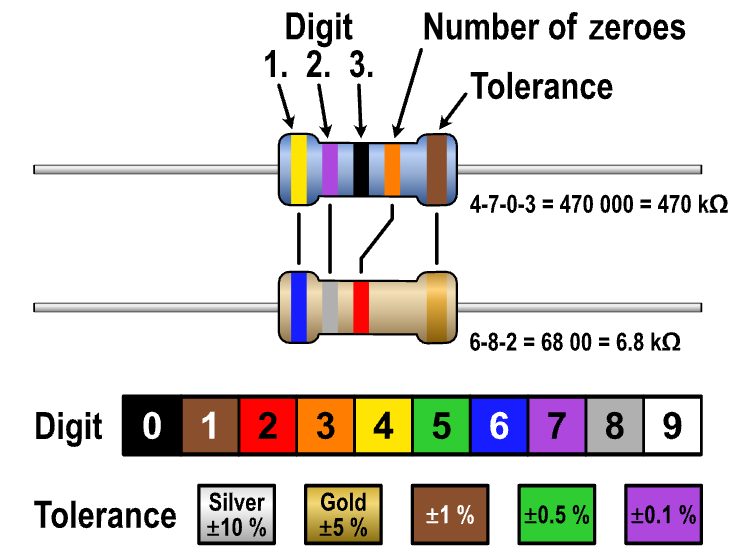
The lines on a resistor are known as color bands, and they represent the resistor’s value and tolerance. Resistors commonly have 4 bands and 5 bands, and we will explain using the 4-band system.
To identify the resistor value, you need to look at the color of the bands. The first two bands represent the significant digits of the resistance value, while the third band represents the multiplier. The fourth band represents the tolerance of the resistor.
Here is a guide to interpreting the color bands on a resistor:
- The first band represents the first significant digit of the resistance value.
- The second band represents the second significant digit of the resistance value.
- The third band represents the multiplier, which is the number of zeros that follow the significant digits.
- The fourth band represents the tolerance of the resistor, which indicates the range within which the actual resistance value may vary from the stated value.
There are also some additional markings that may be present on resistors, such as the manufacturer’s logo or part number.
[…] Understanding Resistor Color Codes: What Do the Lines Represent and How to Identify Them? […]