In the ever-evolving world of Java development, the OSGi (Open Service Gateway Initiative) framework has been a game-changer, enabling modular and dynamic applications. One crucial feature of OSGi is service ranking, a mechanism that allows developers to control the selection of services when multiple implementations are available. In this blog, we will dive deep into OSGi service ranking, explore its significance, and understand how to use it effectively in your OSGi-based projects.
Understanding OSGi Services
Before we delve into service ranking, let’s briefly recap what OSGi services are. OSGi is a modular framework that promotes a component-based architecture. In this architecture, applications are composed of loosely coupled, reusable components known as bundles. Bundles can offer services, which are Java objects made available for other bundles to use.
OSGi services provide a flexible way for bundles to interact with each other, allowing them to dynamically discover and consume services offered by other bundles. This dynamic nature is what makes OSGi so powerful and suitable for building modular, extensible, and maintainable applications.
The Need for Service Ranking
In a real-world OSGi application, it’s common to have multiple implementations of the same service interface. Consider a scenario where you have different database drivers or logging implementations. When multiple bundles offer services of the same type, how does the OSGi framework decide which one to use?
This is where service ranking comes into play. Service ranking allows you to specify a priority for services of the same type. The OSGi framework will then choose the service with the highest ranking when resolving dependencies.
How Service Ranking Works
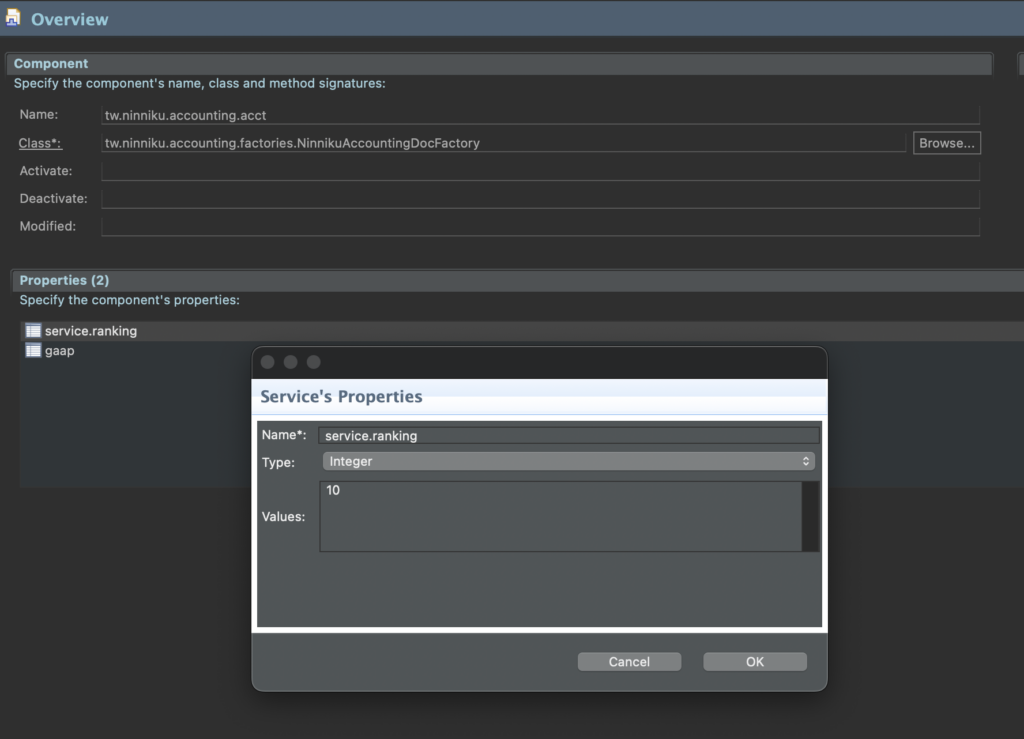
Service ranking is determined by an integer value assigned to each service. The higher the integer value, the higher the service’s rank. By default, services have a ranking of zero. You can set the ranking in Component Definition.
English Version
In the ever-evolving world of Java development, the OSGi (Open Service Gateway Initiative) framework has been a game-changer, enabling modular and dynamic applications. One crucial feature of OSGi is service ranking, a mechanism that allows developers to control the selection of services when multiple implementations are available. In this blog, we will dive deep into OSGi service ranking, explore its significance, and understand how to use it effectively in your OSGi-based projects.
Understanding OSGi Services
Before we delve into service ranking, let’s briefly recap what OSGi services are. OSGi is a modular framework that promotes a component-based architecture. In this architecture, applications are composed of loosely coupled, reusable components known as bundles. Bundles can offer services, which are Java objects made available for other bundles to use.
OSGi services provide a flexible way for bundles to interact with each other, allowing them to dynamically discover and consume services offered by other bundles. This dynamic nature is what makes OSGi so powerful and suitable for building modular, extensible, and maintainable applications.
The Need for Service Ranking
In a real-world OSGi application, it’s common to have multiple implementations of the same service interface. Consider a scenario where you have different database drivers or logging implementations. When multiple bundles offer services of the same type, how does the OSGi framework decide which one to use?
This is where service ranking comes into play. Service ranking allows you to specify a priority for services of the same type. The OSGi framework will then choose the service with the highest ranking when resolving dependencies.
How Service Ranking Works
Service ranking is determined by an integer value assigned to each service. The higher the integer value, the higher the service’s rank. By default, services have a ranking of zero. You can set the ranking in Component Definition.

日本語版
進化し続けるJava開発の世界において、OSGi(Open Service Gateway Initiative)フレームワークは、モジュール式で動的なアプリケーションを実現する画期的な技術です。OSGiの重要な機能の一つがサービスランキングであり、複数の実装が利用可能な場合にサービスの選択を制御できるメカニズムです。このブログでは、OSGiサービスランキングについて深く掘り下げ、その重要性を探り、OSGiベースのプロジェクトで効果的に使用する方法を理解します。
OSGiサービスの理解
サービスランキングに入る前に、OSGiサービスとは何かを簡単に振り返りましょう。OSGiはコンポーネントベースのアーキテクチャを推進するモジュラーフレームワークです。このアーキテクチャでは、アプリケーションはバンドルと呼ばれる疎結合で再利用可能なコンポーネントで構成されます。バンドルはサービスを提供でき、これらは他のバンドルが使用できるようにされたJavaオブジェクトです。
OSGiサービスは、バンドル間の柔軟なインタラクション方法を提供し、他のバンドルが提供するサービスを動的に検出して利用できるようにします。この動的な性質こそが、OSGiをモジュール式で拡張性のある、メンテナンスしやすいアプリケーションの構築に適したものにしています。
サービスランキングの必要性
実際のOSGiアプリケーションでは、同じサービスインターフェースの複数の実装を持つことが一般的です。異なるデータベースドライバやロギング実装があるシナリオを考えてみてください。複数のバンドルが同じタイプのサービスを提供する場合、OSGiフレームワークはどのサービスを使用するかをどのように決定するのでしょうか?
ここでサービスランキングが重要になります。サービスランキングを使用すると、同じタイプのサービスに優先順位を指定できます。OSGiフレームワークは、依存関係を解決する際に最もランキングの高いサービスを選択します。
サービスランキングの仕組み
サービスランキングは、各サービスに割り当てられた整数値によって決定されます。整数値が大きいほど、サービスのランクが高くなります。デフォルトでは、サービスのランキングはゼロです。コンポーネント定義でランキングを設定できます。



